The UN Guiding Principles’ Influence on Supply Chain Due Diligence Laws
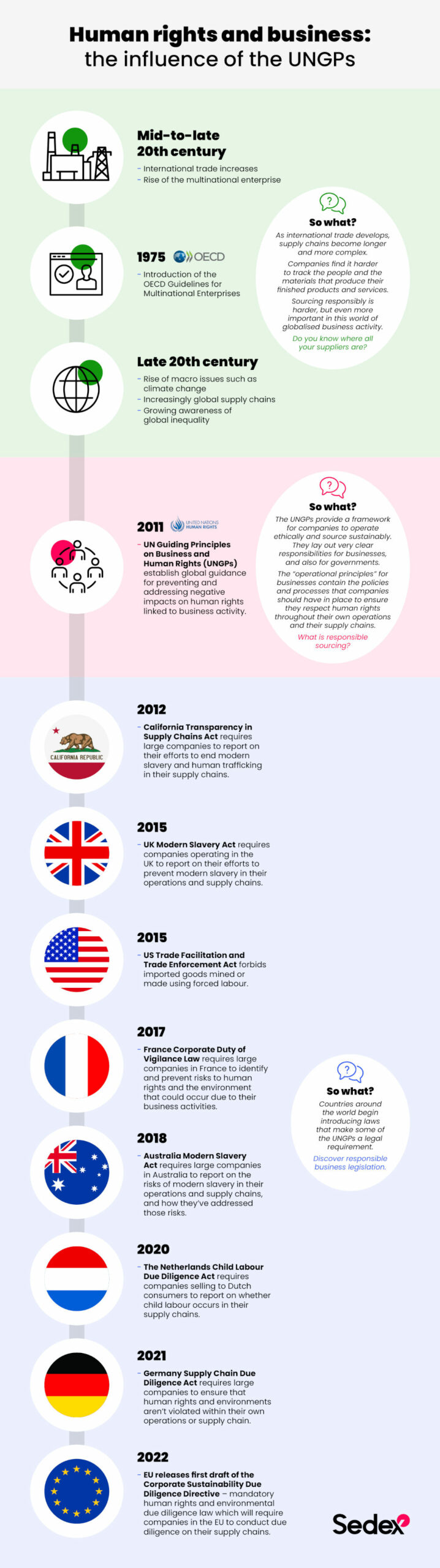
In 2021, the United Nations introduced guidelines for businesses to operate and source responsibly. Explore our visual timeline about the landmark Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, and the human rights due diligence laws they’ve influenced over the past decade.
2021 saw the 10-year anniversary of the United Nations’ landmark guidelines to help businesses respect human rights in their activities and supply chains. The Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (the UNGPs) provide a framework for companies to operate ethically and sustainably, with responsibilities laid out for both businesses and governments. The core principles align with the UN’s human rights due diligence policy and approach for their own organisation.
The UNGPs are a voluntary framework. But since they were introduced in 2011, countries around the world have brought in laws that make some of the Guiding Principles a legal requirement for businesses.
Explore our visual timeline to learn more.
What’s next for businesses and the UNGPs? Get the Ethical Trading Initiative (ETI)’s perspective here.
Other drivers of supply chain due diligence
Alongside legislation for corporate human rights and environmental due diligence, other drivers are also requiring companies to actively address sustainability issues in their supply chains.
- Global factors such as the climate crisis and its impacts, geopolitical tensions and regional conflicts – and greater awareness of all these in the age of information.
- Investors increasingly recognise the operational, reputational and financial impacts of ESG risks and want to make sure the companies they invest in are managing these effectively.
- Consumers, aware of global crises and inequalities, want to know where their money is going. They expect greater transparency from brands about how they operate and where they buy from, to help reassure consumers that they aren’t funding unethical practices.
- Media scrutiny on companies’ operations and supply chains, in response to the above stakeholders’ interests and demands.
Many of the laws outlined above reflect several of these demands, such as the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act. This specifies some issues that companies have to report on, including high-profile topics like modern slavery, waste management and food insecurity.
How Sedex can help your business follow the UNGPs
We support our customers to conduct supply chain due diligence and operate in line with the UN due diligence recommendations outlined in the UNGPs. Our tools and services enable businesses to understand and mitigate the risks of negative impacts and drive sustainability in their supply chains.
Our solutions include:
- Supply chain assessment and auditing – understand the people, practices, environments and conditions across global supply networks.
- Risk assessment – identify, analyse and prioritise social and environmental risks across a supply chain.
- Analysis and reporting on supply chain data to demonstrate improvements and continued positive progress.
- Consulting to provide tailored support for your company’s sustainability-related needs – from programme planning to legislation diagnostics.
- Training to build your knowledge on sustainability and supply chain risk.



